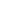This SERIES of pumps specially adopts the open channel impeller, the sewage capacity is super strong...
- E-mail us: lonkey@lonkey.com
- 24 Hour Service - 7 Days a Week
English
Sewage Submersible Pump Manufacturers
Sewage Submersible Pump Industry Knowledge Extension
What Is Sewage Submersible Pump?
A sewage submersible pump is a water pump designed to draw sewage from ponds, rivers, puddles, ditches, sewers, etc. And discharge it to the next treatment station. These pumps are often referred to as "submersible pumps" or "sewage pumps".
These pumps are submersible, so they can get dirty water out without taking up any space. Such pumps typically use an enclosed motor and pump casing to prevent water and dirt from entering the motor, reducing maintenance requirements and extending life. Since they often handle solid particles and other contaminants, they often have high-efficiency filtration systems to prevent these solid particles and contaminants from damaging pumps and piping.
Sewage submersible pumps are commonly used in municipal and industrial areas to transport sewage to treatment sites for treatment.
What Are the Main Features and Advantages of Sewage Submersible Pump?
The sewage submersible pump is a pump that works in water and has the following main features and advantages:
1. High reliability: Due to its design and structure, sewage submersible pump can maintain high reliability when working in water, and is not prone to failure and downtime.
2. Wide applicability: Sewage submersible pump is suitable for many different water environments, including ponds, rivers, puddles, and so on.
3. Strong processing capacity: Sewage submersible pump can handle different types of sewage, including domestic, industrial, municipal sewage, etc., and can effectively discharge sewage to designated locations.
4. Energy saving and environmental protection: Sewage submersible pump has high operating efficiency, which can save energy and reduce pollution and damage to the environment.
5. Safe and reliable: Sewage submersible pump has a complete protection mechanism and automatic control system, which can ensure safety and reliability during the working process.
6. Easy maintenance: Sewage submersible pump is designed with a simple structure, easy to maintain and maintain, which can prolong the life of the pump and improve the efficiency of use.
How about the performance of Sewage Submersible Pump?
1.Flow Rate (Capacity): The flow rate, often measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per second (L/s), indicates how much sewage or wastewater the pump can move within a specific time frame. The flow rate should match the system's requirements to ensure proper waste disposal and prevent backups.
2.Total Dynamic Head (TDH): TDH represents the total resistance that the pump must overcome to move sewage from the source to its final destination, including elevation changes, pipe friction, and other factors. It's measured in feet or meters. Selecting a pump with an appropriate TDH rating ensures it can handle the required pressure to move sewage effectively.
3.Pump Curve: The pump curve graphically represents the relationship between flow rate and TDH for a specific sewage submersible pump. This curve helps you understand how the pump's performance changes at different flow rates and head levels.
4.Efficiency: Pump efficiency indicates how effectively the pump converts input power (electricity) into hydraulic energy (flow and head). Higher efficiency pumps consume less energy for the same amount of work, resulting in lower operational costs over time.
5.Solids Handling Capacity: Sewage contains solid particles, debris, and sediment. The pump's solids handling capacity determines its ability to handle these solids without clogging or damaging the impeller. Consider the maximum solid size the pump can handle and whether it features a solids-handling impeller design.
6.NPSHr (Net Positive Suction Head Required): NPSHr is the minimum suction head required to prevent cavitation within the pump. Ensuring that the available NPSHa (Net Positive Suction Head Available) exceeds the NPSHr of the pump is crucial for preventing cavitation-related issues.
7.Materials of Construction: Sewage pumps should be constructed with materials that can resist corrosion, abrasion, and chemical exposure. Stainless steel and high-quality plastics are commonly used to ensure durability in harsh wastewater environments.
8.Motor Power and Type: The pump's motor power, measured in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW), affects its ability to deliver the required flow and head. The type of motor (single-phase or three-phase) should match the available power supply.
9.Reliability and Longevity: Pumps designed for sewage applications should be reliable and durable. Consider factors like motor protection features, sealing mechanisms, and the quality of internal components.
10.Installation and Maintenance: Ease of installation, maintenance requirements, and access to replacement parts should be considered to ensure convenient and cost-effective operation.
 English
English Español
Español



 +86-576-86330112
+86-576-86330112