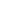LPS circulating pumps are designed for circulating liquids in heating and air conditioning systems a...
- E-mail us: lonkey@lonkey.com
- 24 Hour Service - 7 Days a Week
English
LPS Circulation Pump Manufacturers
-
LPS40-8S/180 Booster Water Pressure Pumps 260W 220V Smart Hot Water Circulation Circulating Pump
Read MoreThe Circulator Pump LPS40-8S is designed to circulate fluids in heating, cooling, air conditioning, ...
LPS Circulation Pump Industry Knowledge Extension
What Is LPS Circulation Pump?
LPS circulation pump is a pump for water circulation, usually used in heating systems, air conditioning systems and industrial equipment. Its main function is to draw water from one container or pipe, and then transport it to another container or pipe through the pipe, thus forming a water cycle.
LPS circulation pumps usually use an electric motor to drive the rotation of the impeller, which creates water flow. These pumps are designed to be lightweight, compact and often have an energy-efficient design that saves energy. In addition, LPS circulating pumps usually feature low noise, low vibration, high reliability, and easy maintenance.
What Are the Structural Features of LPS Circulation Pump?
The structural characteristics of the LPS circulating pump mainly include the following aspects:
1. Pump body: generally made of cast iron or stainless steel, which has good corrosion resistance and compressive strength. There are inlets and outlets inside the pump body, and accessories such as matching pipelines and valves are usually set up.
2. Impeller: The core part of the pump, generally made of corrosion-resistant stainless steel. There are blades inside the impeller, which are rotated by a motor to generate water flow.
3. Motor: It provides power for the LPS circulating pump, and generally adopts a closed fan cooling method to ensure the stable operation of the motor for a long time. The parameters such as the power and speed of the motor will be selected according to different usage requirements.
4. Mechanical seal: It is used to prevent the water flow inside the pump body from leaking out, and is usually made of materials such as hard alloy or ceramics. The quality of the mechanical seal has a great influence on the service life and performance of the pump.
5. Control system: LPS circulating pumps are usually equipped with an electronic control system for automatic control. This control system can realize the functions of pump start and stop, current protection, water level control and so on.
6. Anti-vibration pads: LPS circulating pumps are usually equipped with anti-vibration pads to reduce the vibration and noise generated by the pump during operation. Anti-vibration pads are generally made of materials such as rubber or polyurethane.
What is the working principle of LPS Circulation Pump?
1.Circulation and Stagnation Prevention: In sewage and wastewater systems, maintaining proper circulation is essential to prevent the accumulation of stagnant water. Stagnation can lead to odors, microbial growth, and other issues. LPS Circulation Pumps are designed to facilitate the movement of sewage at lower pressure levels, keeping the flow active and preventing stagnation.
2.Low-Pressure Operation: Unlike high-pressure pumps that are designed to generate significant pressure to overcome resistance, LPS Circulation Pumps operate at lower pressure levels. They are specifically designed to handle the lower pressures commonly found in sewage and wastewater systems.
3.Continuous Operation: LPS Circulation Pumps are often designed for continuous operation, ensuring a steady flow of sewage or wastewater through the system. This helps maintain proper sewage flow, preventing blockages and maintaining system efficiency.
4.Impeller Action: The pump's impeller, a rotating component with curved blades, is responsible for generating the flow of sewage. As the impeller rotates, it imparts kinetic energy to the sewage, causing it to move and circulate through the system.
5.Pressure Differential: While the pressure generated by LPS Circulation Pumps is lower than that of high-pressure pumps, there is still a pressure differential created between the pump's inlet and outlet. This pressure differential drives the sewage flow.
6.Efficient Flow: The impeller design and pump configuration are optimized for efficient flow at lower pressure levels. The goal is to achieve sufficient circulation while avoiding unnecessary energy consumption.
7.Preventing Stagnation Zones: LPS Circulation Pumps are strategically placed in areas of the sewage system where stagnant zones are likely to form. By providing continuous circulation, these pumps help prevent the buildup of debris, sediment, and other materials that could lead to blockages.
 English
English Español
Español



 +86-576-86330112
+86-576-86330112